Do you have a desire to find a deeper understanding of yourself? Are you on a journey toward personal discovery? Are you curious to find out part of what makes you tick as an individual? Then the Enneagram may be what you’ve been looking for.
What Is The Enneagram?
The Enneagram is a powerful tool for your personal transformation. The word ‘enneagram’ stems from the Greek words ennea, meaning nine, and grammos, meaning a written symbol.
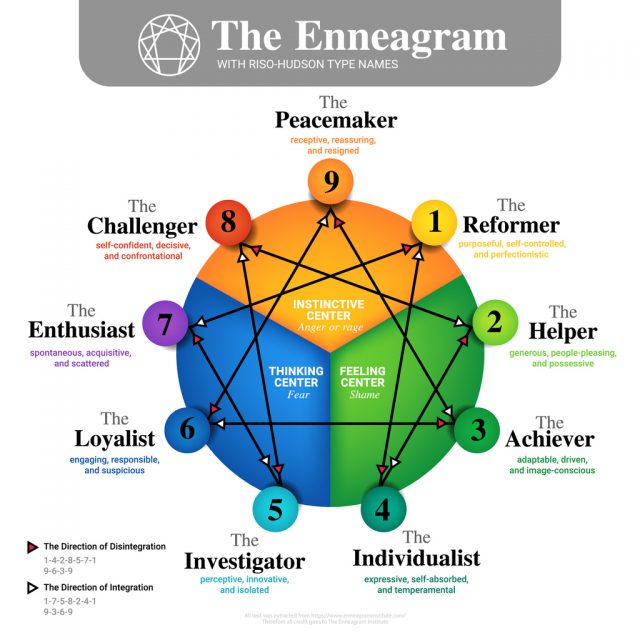
The nine-pointed Enneagram symbol represents strategies for relating to yourself, others, and the world. Each of the nine Enneagram types has a different way of thinking, feeling, and acting. These differences arise from deeper motivation and/or worldview.
How to Discover Your Enneagram Type
According to The Enneagram Institute, everyone is born with a dominant type. This type is established in childhood. We do not change from one basic personality type to another. The descriptions are universal. However, not everything in the description will apply to you all the time. Also, none of the personality types are inherently better or worse than any of the others. Each type carries its own unique assets as well as liabilities.
The Enneagram Institute offers, for a fee, for you to take their Riso-Hudson Enneagram Type Indicator (RHETI) Test. (There are also free tests available online. However, they aren’t as in-depth as the one offered by the Institute.) The RHETI, when taken properly, will identify your basic personality type for you.
What are the nine personality types of the Enneagram?
Type 1: The Reformer
The Reformer is described as principled, purposeful, self-controlled, and perfectionistic. They’re very conscientious and ethical and often advocate for change. They’re constantly trying to improve things, but they’re also terrified of making mistakes. They typically have problems with resentment and impatience.
Basic Fear: Of being evil or defective
Basic Desire: To be good and balanced
Key Motivations: Ones always want to be right, to strive higher, and improve everything.
Type 2: The Helper
Helpers are generous, demonstrative, people-pleasing, and possessive. They are driven to be close to others, but they can end up doing things for others too much. They tend to have issues with possessiveness and with acknowledging their own needs.
Basic Fear: Of being unworthy of love
Basic Desire: To feel loved
Key Motivations: Twos love to be needed and appreciated and for others to vindicate their claims about themselves.
Type 3: The Achiever
The Achiever is known for being adaptable, excelling, driven, and image-conscious. They can also be status-conscious and highly driven for advancement. They are diplomatic and poised but can be overly concerned with what people think of them.
Basic Fear: Of being worthless
Basic Desire: To feel valued
Key Motivations: Achievers need to distinguish themselves from others, to have attention, to be admired, and to impress others.
Type 4: The Individualist
Individualists are expressive, dramatic, self-absorbed, and temperamental. They are also emotionally honest, creative, and personal, but can also be moody and self-conscious. They typically have problems with melancholy and self-indulgence.
Basic Fear: That they have no identity
Basic Desire: To find themselves and their significance
Key Motivations: Fours want to express themselves and their individuality, and to create and surround themselves with beauty.
Type 5: The Investigator
Investigators are perceptive, innovative, secretive, and isolated. They can also become preoccupied with their thoughts and imaginary constructs, which can make them detached and intense. They typically have problems with eccentricity, nihilism, and isolation.
Basic Fear: Being useless, helpless, or incapable
Basic Desire: To be capable and competent
Key Motivations: Fives need to possess knowledge, to understand the environment, to have everything figured out as a way of defending the self from threats from the environment.
Type 6: The Loyalist
Loyalists are known to be engaging, responsible, anxious, and suspicious. They are reliable and excellent “troubleshooters,” they foresee problems and foster cooperation, but can also become defensive, evasive, and anxious — running on stress while complaining about it.
Basic Fear: Of being without support and guidance
Basic Desire: To have security and support
Key Motivations: Want to have security, to feel supported by others, to have certitude and reassurance, to test the attitudes of others toward them, to fight against anxiety and insecurity.
Type 7: The Enthusiast
Sevens are spontaneous, versatile, acquisitive, and scattered. They tend to misapply their many talents, becoming over-extended, scattered, and undisciplined. They typically have problems with impatience and impulsiveness.
Basic Fear: Of being deprived and in pain
Basic Desire: To be satisfied and content—to have their needs fulfilled
Key Motivations: Want to maintain their freedom and happiness, to avoid missing out on worthwhile experiences, to keep themselves excited and occupied, to avoid and discharge pain.
Type 8: The Challenger
Eights are self-confident, decisive, willful, and confrontational. They are protective, resourceful, straight-talking, and decisive, but can also be ego-centric and domineering. They typically have problems with their tempers and with allowing themselves to be vulnerable.
Basic Fear: Of being harmed or controlled by others
Basic Desire: To protect themselves (to be in control of their own life)
Key Motivations: Eights want to be self-reliant, to prove their strength and resist weakness, to be important in their world, to dominate the environment, and to stay in control of their situation.
Type 9: The Peacemaker
Peacemakers are receptive, reassuring, complacent, and resigned. They are usually creative, optimistic, and supportive, but can also be too willing to go along with others to keep the peace. They typically have problems with inertia and stubbornness.
Basic Fear: Of loss and separation
Basic Desire: To have inner stability “peace of mind”
Key Motivations: Want to create harmony in their environment, to avoid conflicts and tension, to preserve things as they are, to resist whatever would upset or disturb them.
None of us are purely one personality type. Everyone is a unique mix of their basic personality type and usually one of the two types adjacent to it. This is your wing. Your personality is dominated by your basic type. The wing complements it and adds important, and sometimes contradictory elements. There are those that believe individuals have two wings. Generally speaking though, one wing will be more dominant than the other.
Just Remember
The Enneagram is open-ended and highly dynamic. But it doesn’t say all there is to say about human beings. The reality is, people are only understandable to a certain point. Beyond that point, they remain mysterious and unpredictable. This reality is one of the beauties of life. The Enneagram may not be able to unlock all the mysteries of life. But it can give us a deeper understanding of who we are. And it gives us clarity and meaning about ourselves as individuals.
Research shows that when couples connect psychologically, they connect biologically too. Read more about attachment theory and how it can affect your relationships.







