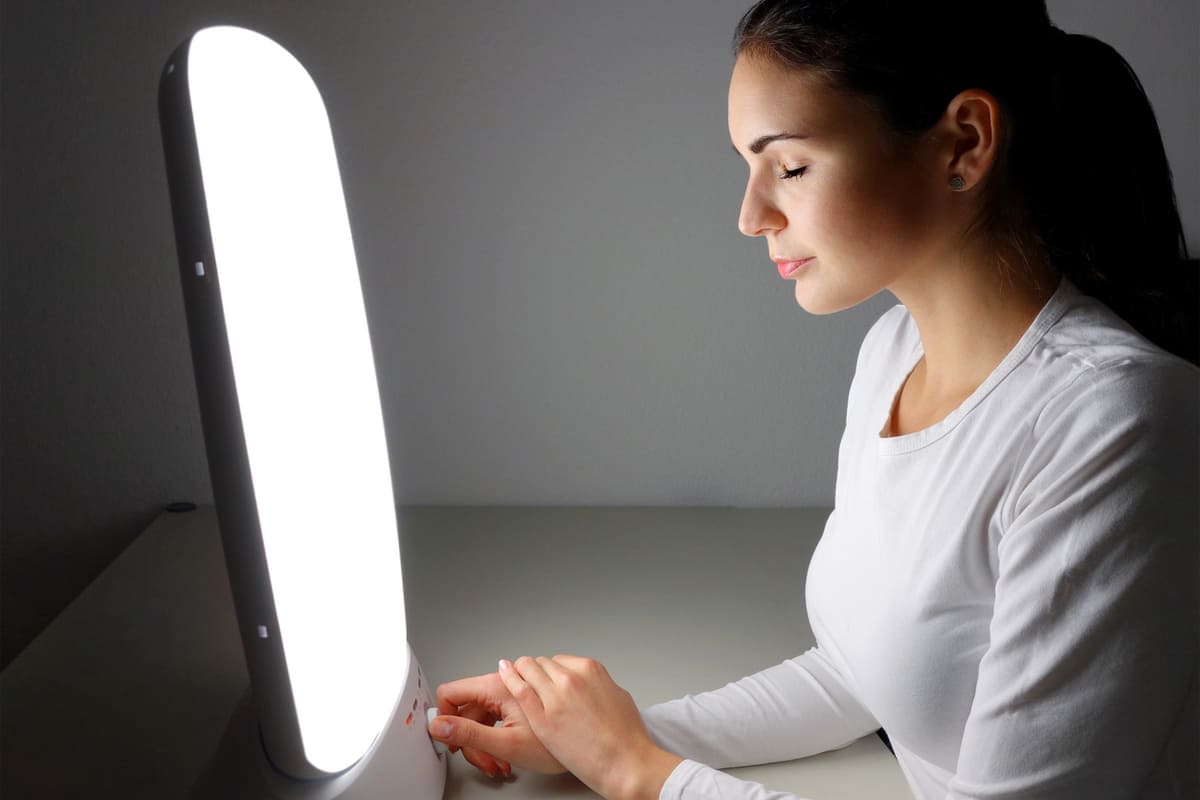
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a significant role in the absorption of calcium and phosphorous, which are vital to bone and dental health as well as normal immune function. Your body will only create vitamin D when it’s exposed to sunlight. However, this essential vitamin can also be sourced from food and supplements.
People that don’t go outside much or live in climates with limited sunlight may struggle to get the vitamin D they need. It’s important to note that medical conditions can also cause a deficiency. Symptoms include tiredness, aches and pains in the bones and muscles, general weakness, and an increased risk of fractures.
You can do a few things to overcome a vitamin D deficiency, and light therapy is being more commonly looked at as a solution. This article will explore light therapy techniques and the benefits they can provide.
What is Light Therapy?

Light therapy involves using a UV lamp that emits ultraviolet radiation similar to that found in sunlight. It is useful in helping people with a deficiency produce vitamin D. It is available for commercial home use, and a doctor could also prescribe it.
Does Light Therapy Work?
A 2007 study focused on people with cystic fibrosis (CF) and short bowel syndrome (SBS), both of which are conditions that are associated with a vitamin D deficiency. They used UV indoor tanning lamps that mimic natural sunlight to determine how effective they could be in circulating vitamin D throughout the body.
The study involved two SBS subjects coming to an outpatient clinic twice a week for a total of six weeks for six-minute UV light sessions.
A follow-up study brought in five CF subjects who exposed their lower back areas to the UV light while seated at a distance of 14 centimeters from the source. Exposure lasted 5-10 minutes depending on skin type, and sessions took place five times a week for eight weeks.
Blood samples were taken before and after the study to test for levels of vitamin D and the parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Results revealed that the lamps effectively increased or maintained the circulation of vitamin D throughout the body in SBS patients. An increased UV lamp frequency was also beneficial to vitamin D circulation in CF patients, and PTH levels remained mostly unchanged in both groups.
What does this all mean? The study shows UV lamps have the potential to be an alternative treatment method for patients dealing with cystic fibrosis and short bowel syndrome and may be prescribed to them in the future.
Other Benefits of UV Therapy

UV therapy is excellent for aiding with vitamin D deficiency. It may also provide other benefits, including the following:
Beneficial to Skin Conditions
UV radiation may be helpful in the treatment of eczema, dermatitis, jaundice, scleroderma, and psoriasis.
Improves Mood
Light therapy may improve mood and can be useful in treating Seasonal Affective Disorder.
Good for Heart Health
The vitamin D in UV rays can lower blood pressure, making them beneficial to heart health.
Increases Melanin
UV exposure may increase melanin (brown pigmentation) in the skin, which protects against DNA damage.
Sterilization and Disinfection
UV radiation can be used alongside other techniques to sterilize tools and workspaces in medical and biology labs.
Air Purification
UV rays can destroy DNA in micro-organisms. Emitters are often used alongside purification systems to assist in cleaning the air.
Risks and Side Effects
Like the sun, UV rays can cause sunburn and skin cancer. Light therapy should only be used as directed.
Other Ways to Increase Vitamin D Levels

Light therapy is a good way to fight a vitamin D deficiency, but it’s not the only solution out there. Here are some other ways to ensure you get the vitamin D you need.
- Get More Sunlight: Going out in the sun for 15 -20 minutes a day, three days a week, can help you get the vitamin D you require.
- Eating the Right Foods: You may try changing up your diet to eat more foods that are rich in vitamin D. These include dairy products and orange juice fortified with vitamin D, seafood like salmon, swordfish, tuna, and sardines, and beef liver.
- Take a Supplement: If you are having difficulty adding vitamin D-rich foods to your diet, you may want to take a supplement instead. A dose of 600 to 800 IUs a day is recommended, depending on your age.
- Medications: If you go to a doctor for treatment for your vitamin deficiency, he or she may prescribe medications such as laxatives, steroids, cholesterol-lowering drugs, seizure-control drugs, and more.
A vitamin D deficiency is a condition no one wants to have. Fortunately, light therapy and other forms of treatment can help you get the vitamin D you need. What methods will you be using to ensure you get enough of this vital nutrient?
Increase Your Vitamin D Levels At Home






Read Next:
Are You Getting Enough Vitamin D in Your Diet?