When it comes to vitamins, C and D often take center stage, but vitamin B also deserves your attention. Vitamin B-12 is considered especially important to your health, and it’s essential for the creation of red blood cells and many other critical body processes. It’s important to avoid a vitamin B12 deficiency; luckily, you don’t need much. Just 2.4 milligrams a day for most adults is enough, yet you may be coming up short.
Why is B12 so important?

As we mentioned earlier, your body needs vitamin B12 to make red blood cells. It’s also critical for your nerves, your DNA, and to carry out other functions. Unfortunately, vitamin B12 can’t be made by the body. You need to get your intake from food and supplements. That’s tough to do for some people with special diets or if they’re on medication that prevents absorption. A B12 deficiency is actually relatively common because of this, especially in older people. By older, we mean 50 and up.
What’s the harm of B12 Deficiency?
A case report from Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital was published in The New England Journal of Medicine outlining just how bad it can get if your body doesn’t have enough B12. In this case, over the course of two months, a 62-year-old man experienced all of the following issues: Numbness and a “pins and needles” sensation in his hands, trouble walking, and severe joint pain. He also started turning yellow and became progressively short of breath. The cause was a lack of vitamin B12 in his bloodstream. Additionally, the report explained that it could’ve been worse. A more severe case of B12 deficiency could even lead to deep depression, paranoia and delusions, memory loss, incontinence, loss of taste and smell, and more.
Who is most at risk of B12 Deficiency?
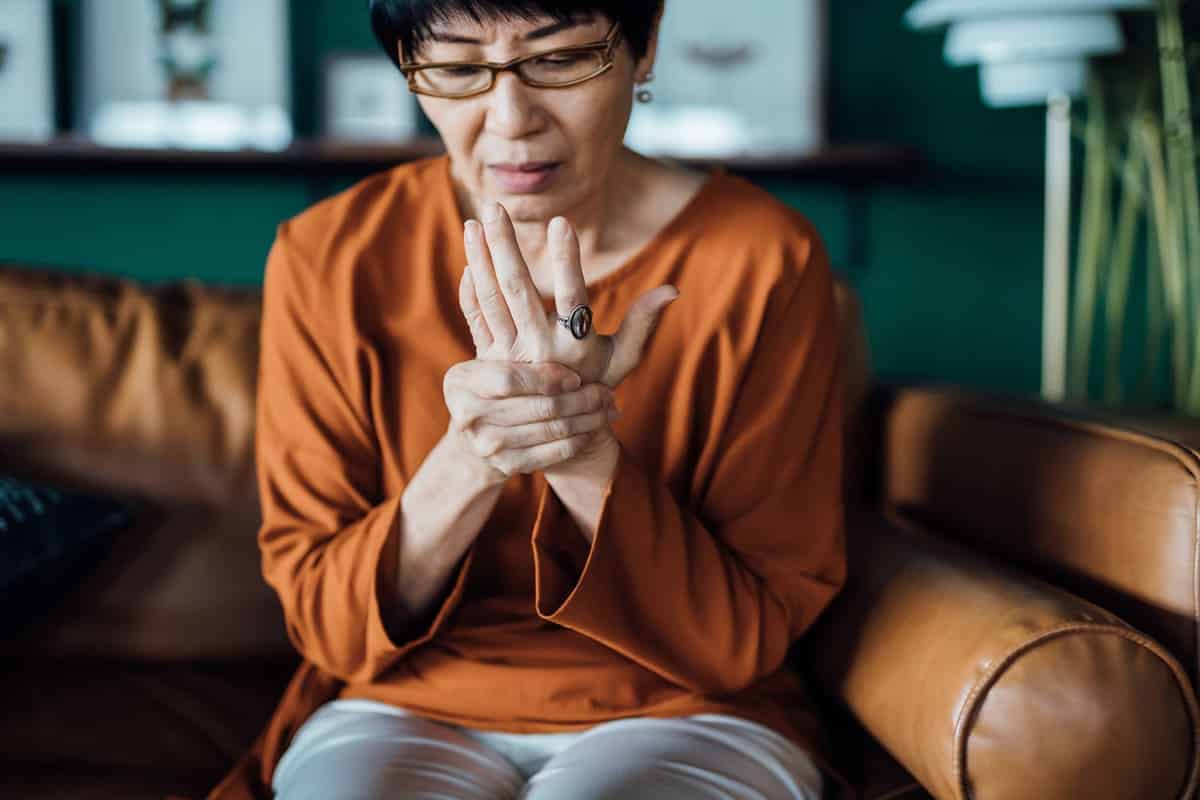

People on vegetarian diets are most at risk of a vitamin B12 deficiency, along with those with weight-loss surgery. Why is that? You can’t get B12 from plants, so vegans and vegetarians have to be especially cautious. It comes from meat, eggs, poultry, dairy products, and other foods from animals. To make sure they get enough, vegans and vegetarians need to eat grains that have been fortified with the vitamin or take a vitamin supplement.
People who’ve undergone weight-loss surgery also need to be cautious because the surgery interferes with the body’s ability to get B12 from food. People with certain conditions, like celiac or Crohn’s disease, also face issues because those conditions interfere with nutrient absorption. Also, people taking commonly prescribed heartburn drugs need to be careful since the drugs reduce acid production in the stomach, and the acid is essential for B12 absorption. People over 50 are also at risk since acid production in the stomach slows with aging.
How do I know if I have a B12 deficiency?
Potential warning signs of a vitamin B12 deficiency include emotional or cognitive struggles, fatigue, weakness, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. You may also have balance problems or issues walking. However, those could be issues you see in several other conditions, so you’ll need a blood test to diagnose a deficiency. It’s important to detect and treat it quickly, or you risk severe neurological problems and blood diseases.
How to Prevent B12 Deficiency
If you aren’t getting enough with your normal diet, or you have conditions preventing absorption, you can increase your levels with fortified soy foods or grain products, including cereal. Vitamin supplements can also help. In most mild cases, a simple multivitamin will be ample. Serious issues can be corrected with weekly B12 shots or daily high-dose pills.
In many people, a vitamin B12 deficiency can be prevented. If you are a strict vegetarian or vegan, it’s important to eat bread, cereals, or other grains that have been fortified with vitamin B12 or take a daily supplement. A standard multivitamin delivers 6 micrograms, more than enough to cover the average body’s daily needs.
It’s not a cure-all

There are articles all over the internet identifying vitamin B12 as a possible treatment and prevention for a number of conditions, from Alzheimer’s disease to infertility. Others include heart disease, eczema, and a long list of other health problems. Heck, even this writer has taken it for fatigue, with the hope that it’ll somehow inject me with enough energy to combat day-to-day exhaustion from raising four children, working, and all the other stresses the world likes to serve up. I’ve even gone as far as getting the weekly injections mentioned earlier. Did it work? Maybe. Or maybe it was a placebo effect that just convinced me I was less depleted. Anyone who’s been as wiped out as I’ve been is eager to find a solution.
The point, though, is there’s not always evidence to back up the promises. There is, however, evidence that you need to be aware of your levels and do what you can to maintain them before you end up with a B12 deficiency. If your B12 levels are low, make the changes to be sure they don’t stay that way.
B12 Supplements


Read Next:
Could one daily vitamin help you avoid Alzheimer’s as you age? A new study offers hope.







